리눅스
ifconfig eth0 down hw ether aa:bb:cc:dd:ee:ff
ifconfig eth0 up
윈도우
아래를 보시오;ㅁ;
Changing Your MAC Address In Window XP/Vista, Linux And Mac OS X
(Sometimes known as MAC spoofing)
First let me explain a few things about MAC addresses. MAC stands for Media Access Control and in a sense the MAC address is a computer뭩 true name on a LAN. An Ethernet MAC address is a six byte number, usually expressed as a twelve digit hexadecimal number (Example: 1AB4C234AB1F).
IPs are translated to MAC address by a protocol called ARP (Address Resolution Protocol). Let뭩 say a computer with and IP of 192.168.1.1 wants to send information to another computer on the LAN that has an IP of 192.168.1.2 . First 192.168.1.1 will send out a broadcast to all stations on the LAN asking who has the IP 192.168.1.2. Then the box that has 192.168.1.2 will respond to 192.168.1.1 with it뭩 MAC address which is cached in 192.168.1.1뭩 ARP table for later use. To put this in Socratic Dialog form (with just a touch of Stallone):
Host 1 (192.168.1.1): Yo everyone on the LAN (FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF), who has the IP 192.168.1.2? My MAC is DE:AD:BE:EF:CA:FE so you can respond back to me.
Host 2 (192.168.1.2): Hello DE:AD:BE:EF:CA:FE, I have IP 192.168.1.2 and my MAC address is 12:34:56:78:90:12 so you can send your IP packets to me.
You can see the ARP table of a box by dropping out to a command prompt and typing 밶rp 뻕?in Windows or just 밶rp?in Linux. ARP can also work the other way by a host on the LAN sending its MAC address to another machine on the LAN for preemptive caching unless the host is configured to not accept un-requested ARP replies.
A person might want to change the MAC address of a NIC for many reasons:
- To get past MAC address filtering on a router. Valid MAC addresses can be found by sniffing them and then the deviant user could assume the MAC of a valid host. Having two hosts on the same network can cause some network stability problems, but much of the time it's workable. This is one of the reasons why MIC Address filtering on a wireless router is pointless. An attacker can just sniff the MAC address out of the air while in monitor mode and set his WiFi NIC to use it. Interestingly, a lot of hotels use MAC filtering in their "pay to surf" schemes, so this method can be an instant in for cheap skate road warriors.
- Sniffing other connections on the network. By assuming another host's MAC as their own they may receive packets not meant for them. However, ARP poisoning is generally a better method than MAC spoofing to accomplish this task.
- So as to keep their burned in MAC address out of IDS and security logs, thus keeping deviant behavior from being connected to their hardware. For example, two of the main things a DHCP server logs when it leases an IP to a client is the MAC address and host name. If you have a wireless router look around on it's web interface for where it logs this info. Luckily there are tools to randomize this information (MadMACs).
- To pull off a denial of service attack, for instance assuming the MAC of the gateway to a sub net might cause traffic problems. Also, a lot of WiFi routers will lock up if a client tries to connect with the same MAC as the router's BSSID.
Linux
To change your MAC address in Linux (and most *nix system) is easy as pie. All it takes is two easy to script commands:
ifconfig eth0 down hw ether 00:00:00:00:00:01
ifconfig eth0 up
These two little commands would set your eth0 interface to use the MAC 00:00:00:00:00:01. Just plug in the NIC you want to set and the MAC address you want to use into the commands above and your done. Changing your MAC address is one of those things that is much easier to do in Linux then under Windows.
Mac OS X
For versions of OS X before Tiger (OS X 10.4) you will need this patch:
http://slagheap.net/etherspoof/
Then you use a command like:
sudo ifconfig en0 lladdr 00:00:00:00:00:01
I'm not much of a Macintosh guy, so I pulled most of this info from:
http://www.macgeekery.com/gspot/2006-04/mac_address_spoofing
My understanding is that there are complications with some AirPort cards so you may also want to read:
http://rgov.org/airport-spoof/
Windows 2000/XP/Vista: The Hard Way
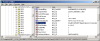
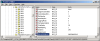
In XP you can use the regedit to edit the registry from a GUI or the reg command to edit it from the console, I뭠l be using regedit. Information on all your NICs can be found the registry key HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\ Class\{4D36E972-E325-11CE-BFC1-08002bE10318}\ . Under this key you will find a bunch of sub keys labeled as 0000, 00001, 0002 and so forth. We can assume any MAC address we want by finding the key that controls the NIC we want to change, putting in a string value called 밡etworkAddress?and setting it to the MAC address we want to use formatted as a twelve digit hex number (example: 000000000001). To find out which key is which we can search through them for the value 밆riverDesc?until we find the one that matches the NIC we wish to alter. After you set 밡etworkAddress?to the address you want just restart the NIC by disabling it then enabling it (or in the case of PCMCIA cards, just eject and reinsert). You can confirm the MAC address change by using the 밽etmac?or 밿pconfig /all?commands.
Windows 2000/XP/Vista: The Easy Way
Use Mac Makeup ( http://www.gorlani.com/publicprj/macmakeup/macmakeup.asp ), MadMACs (http://www.irongeek.com/i.php?page=security/madmacs-mac-spoofer), Smac ( http://www.klcconsulting.net/smac/ ) or Etherchange (http://ntsecurity.nu/toolbox/etherchange/ ). Mac Makeup is a cool little GUI and Command line tool that's freeware, the creator also offers a Plugin for Bart's PE builder. MadMACs is a tool to randomize your MAC address and host name on every reboot. Smac has a nice GUI and was free but has since gone commercial, there's no reason to bother with it as there are free tools that are just as good. I use MadMACs since I wrote it and it lets me keep my host information randomized.
Have fun with your MAC addresses switching, but be careful not to cause network problems. My favorite MAC address is DEADBEEFCAFE, for other interesting MACs see:
http://www.binrev.com/forums/index.php?showtopic=15942
Enjoy.
출처
http://www.irongeek.com/i.php?page=security/changemac
 Catergories
Catergories Recent Articles
Recent Articles Recent Comments
Recent Comments Calendar
Calendar Archive
Archive Link
Link Search
Search



 Linux, Window에서 mac 어드레스 바꾸기
Linux, Window에서 mac 어드레스 바꾸기 






